Merge request pipelines
DETAILS: Tier: Free, Premium, Ultimate Offering: GitLab.com, Self-managed, GitLab Dedicated
Renamed from
pipelines for merge requeststomerge request pipelinesin GitLab 14.8.
You can configure your pipeline to run every time you make changes to the source branch in a merge request.
This type of pipeline, called a merge request pipeline, runs when you:
- Create a new merge request from a source branch that has one or more commits.
- Push a new commit to the source branch for a merge request.
- Go to the Pipelines tab in a merge request and select Run pipeline.
In addition, merge request pipelines:
- Have access to more predefined variables.
- Do not have access to protected variables or protected runners.
These pipelines display a merge request label in pipeline lists.
Merge request pipelines run on the contents of the source branch only, ignoring the content of the target branch. To run a pipeline that tests the result of merging the source and target branches together, use merged results pipelines.
Prerequisites
To use merge request pipelines:
- Your project's
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile must be configured with jobs that run in merge request pipelines. To do this, you can use: - You must have at least the Developer role in the source project to run a merge request pipeline.
- Your repository must be a GitLab repository, not an external repository.
Use rules to add jobs
Use the rules keyword to configure jobs to run in
merge request pipelines. For example:
job1:
script:
- echo "This job runs in merge request pipelines"
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == 'merge_request_event'You can also use the workflow: rules keyword
to configure the entire pipeline to run in merge request pipelines. For example:
workflow:
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == 'merge_request_event'
job1:
script:
- echo "This job runs in merge request pipelines"
job2:
script:
- echo "This job also runs in merge request pipelines"A common workflow configuration is to have pipelines run for merge requests, tags, and the default branch. For example:
workflow:
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == 'merge_request_event'
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TAG
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH
Use only to add jobs
rules is the preferred method, but you can also use
the only keyword with merge_requests
to configure jobs to run in merge request pipelines. For example:
job1:
script:
- echo "This job runs in merge request pipelines"
only:
- merge_requestsUse with forked projects
- Introduced in GitLab 13.3.
- Moved to GitLab Premium in 13.9.
External contributors who work in forks can't create pipelines in the parent project.
A merge request from a fork that is submitted to the parent project triggers a pipeline that:
- Is created and runs in the fork (source) project, not the parent (target) project.
- Uses the fork project's CI/CD configuration, resources, and project CI/CD variables.
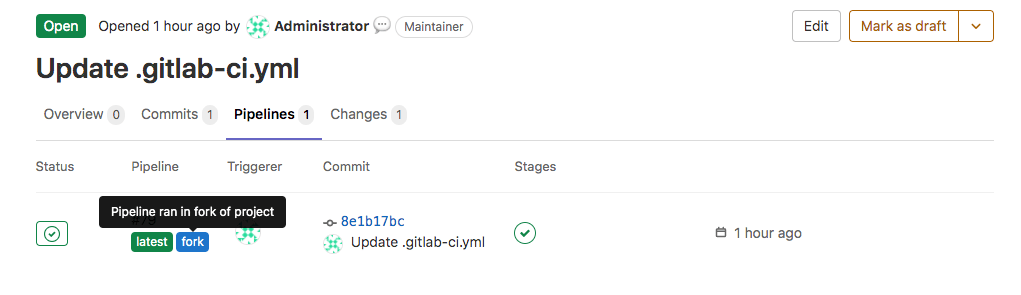
Pipelines for forks display with the fork badge in the parent project:
Run pipelines in the parent project
Project members in the parent project can trigger a merge request pipeline for a merge request submitted from a fork project. This pipeline:
- Is created and runs in the parent (target) project, not the fork (source) project.
- Uses the CI/CD configuration present in the fork project's branch.
- Uses the parent project's CI/CD settings, resources, and project CI/CD variables.
- Uses the permissions of the parent project member that triggers the pipeline.
Run pipelines in fork project MRs to ensure that the post-merge pipeline passes in the parent project. Additionally, if you do not trust the fork project's runner, running the pipeline in the parent project uses the parent project's trusted runners.
WARNING:
Fork merge requests can contain malicious code that tries to steal secrets in the parent project
when the pipeline runs, even before merge. As a reviewer, carefully check the changes
in the merge request before triggering the pipeline. Unless you trigger the pipeline
through the API or the /rebase quick action,
GitLab shows a warning that you must accept before the pipeline runs. Otherwise, no warning displays.
Prerequisites:
- The parent project's
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile must be configured to run jobs in merge request pipelines. - You must be a member of the parent project with permissions to run CI/CD pipelines. You might need additional permissions if the branch is protected.
- The fork project must be visible to the user running the pipeline. Otherwise, the Pipelines tab does not display in the merge request.
To use the UI to run a pipeline in the parent project for a merge request from a fork project:
- In the merge request, go to the Pipelines tab.
- Select Run pipeline. You must read and accept the warning, or the pipeline does not run.
Prevent pipelines from fork projects
- Introduced in GitLab 15.3.
To prevent users from running new pipelines for fork projects in the parent project
use the projects API to disable the ci_allow_fork_pipelines_to_run_in_parent_project
setting.
WARNING: Pipelines created before the setting was disabled are not affected and continue to run. If you rerun a job in an older pipeline, the job uses the same context as when the pipeline was originally created.
Available predefined variables
When you use merge request pipelines, you can use:
- All the same predefined variables that are available in branch pipelines.
- Additional predefined variables available only to jobs in merge request pipelines.